Businessuite News24
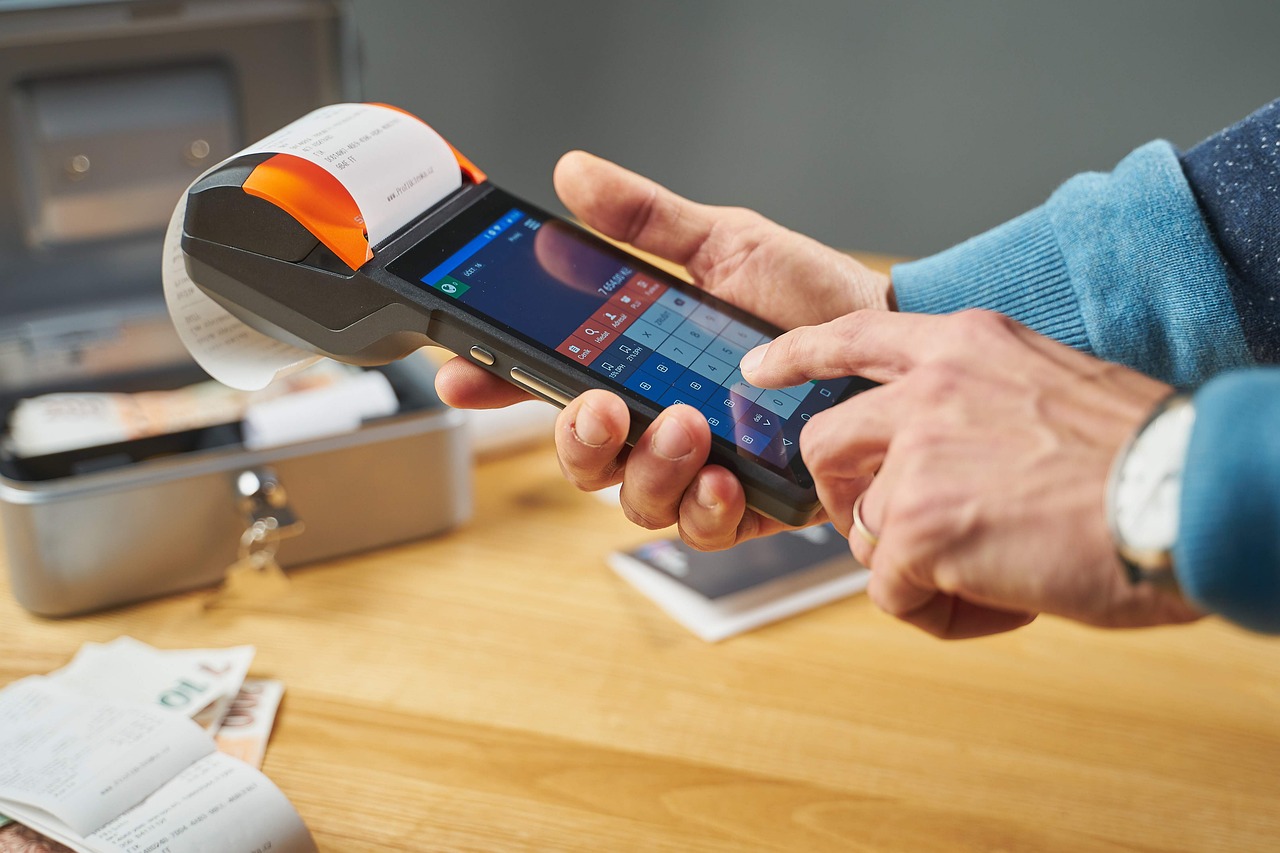
Accelerating Digital Payments and Jamaica’s Push Toward a Cashless Future

Businessuite News24
Businessuite Special Report P4 | Homegrown Disruption: InterMetroONE & Walkbout.com Position Jamaica’s Answer to Uber–Airbnb
Now is the time for SMEs, associations, and government to align—ensuring that if Uber and Airbnb ever arrive together, Jamaica’s own ecosystem remains vibrant and in control.
Businessuite News24
Businessuite Special Report P3 | Uber x Airbnb: A Strategic Alliance That Could Redefine Jamaica’s Travel Industry – But At What Cost?
The future of Jamaican tourism lies in its ability to integrate into global digital ecosystems without sacrificing local livelihoods. The time for public–private dialogue is now.
Businessuite News24
Businessuite Special Report P2 | Disruption in Jamaica: Uber & Airbnb Business Models
Business Insights
Businessuite Special Report P1 | When Titans Unite: How an Uber–Airbnb Alliance Could Redefine Travel in Jamaica and Beyond
“When Uber and Airbnb join forces, travel transforms. But will it uplift local economies or leave them stranded on the roadside of progress?”
Businessuite News24
India’s 10-Minute Delivery Boom: A Blueprint for Disruption—and a Wake-Up Call for Caribbean Courier Companies
While the Caribbean market differs significantly in terms of geography, population density, and infrastructure, India’s 10-minute delivery trend signals a major shift in consumer expectations and service standards that cannot be ignored. Caribbean courier and logistics companies must take this as a call to evolve or risk irrelevance.
-

 Businessuite Markets4 weeks ago
Businessuite Markets4 weeks agoScotia Group Delivers 19% Q2 Profit Growth, Net Income Hits $5B for the Quarter
-

 Businessuite News242 weeks ago
Businessuite News242 weeks agoIndia’s 10-Minute Delivery Boom: A Blueprint for Disruption—and a Wake-Up Call for Caribbean Courier Companies
-

 Businessuite News241 week ago
Businessuite News241 week agoBusinessuite Special Report P4 | Homegrown Disruption: InterMetroONE & Walkbout.com Position Jamaica’s Answer to Uber–Airbnb
-

 Corporate Feature2 weeks ago
Corporate Feature2 weeks agoNot Just Vanity Metrics: A Digital Leader Focused on What Matters
-

 Businessuite News24 International2 weeks ago
Businessuite News24 International2 weeks agoIndia’s 10-Minute Delivery Boom: Reshaping Retail, Logistics, and Urban Spaces
-

 Businessuite Markets1 week ago
Businessuite Markets1 week agoEduFocal Faces Equity Deficit of $135M Amid $314M in Accumulated Losses
-

 Businessuite Women2 weeks ago
Businessuite Women2 weeks agoDorothea Gordon-Smith Marks 50 Years of Quiet Power in Waste Management
-

 Business Insights4 days ago
Business Insights4 days agoBusinessuite Cover Story: Too Much Power? Governance Risks Rise as Tyrone Wilson Consolidates Leadership at Kintyre and Visual Vibe